Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Extending Electric Driving Range
In today’s EV course session, we examined Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)—a vehicle category developed to extend the all-electric driving capability of conventional hybrid vehicles. PHEVs combine the advantages of electric propulsion with the flexibility of an internal combustion engine, making them a practical solution during the transition toward full electrification.
What Is a Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)?
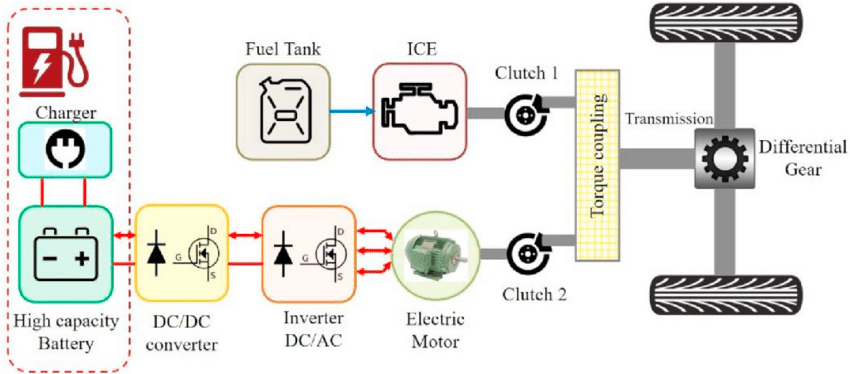
A Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) uses:
- An electric motor and battery pack
- An internal combustion engine (ICE)
- External grid charging capability
Unlike conventional HEVs, electric propulsion is the primary driving mode in PHEVs. As a result, PHEVs require larger battery capacities than HEVs.
Operating Principle of a PHEV
PHEVs are designed to prioritize electric operation:
- Vehicle start: Operates in all-electric mode
- Normal driving: Runs on battery power for daily commuting
- Low battery state of charge: ICE activates to provide propulsion support or recharge the battery
- Extended travel: ICE acts as a range extender, ensuring long-distance capability
In addition to grid charging, PHEVs also recover energy through regenerative braking, improving overall energy efficiency.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Because PHEVs operate in electric mode for most short trips:
- Carbon footprint is lower than HEVs
- Fuel consumption is significantly reduced
- Operating cost decreases due to lower fuel usage
For many users, daily commuting can be completed without using the ICE at all, provided regular charging is available.
Market Adoption of PHEVs
PHEVs are now well-established in the global vehicle market. Popular models include:
- Chevrolet Volt
- Toyota Prius Plug-In
Their success demonstrates strong consumer demand for vehicles that balance electric driving with range security.
Why PHEVs Are Important
From an engineering perspective, PHEVs offer:
- Flexibility of electric and fuel-based propulsion
- Reduced dependence on charging infrastructure compared to BEVs
- A smoother transition path from ICE vehicles to fully electric vehicles
They represent an effective compromise between range anxiety and environmental responsibility.
latest video
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua